T4 and T5 Vertebrae Pain: Understanding Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment

Experiencing pain in the T4 and T5 vertebrae can be distressing and disruptive to daily life. The thoracic spine, which comprises the twelve vertebrae between the cervical and lumbar regions, plays a crucial role in maintaining proper posture and supporting the upper body. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the thoracic spine, identify the causes of T4 and T5 vertebrae pain, discuss symptoms, explore diagnostic methods, and present various treatment options available. With knowledge and timely intervention, individuals suffering from this pain can reclaim their quality of life.
Anatomy of the Thoracic Spine
The thoracic spine consists of T1 to T12 vertebrae, with the T4 and T5 vertebrae located in the middle portion. Each vertebra is separated by intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers. The vertebrae are connected by a series of ligaments and muscles that provide support and allow movement. The thoracic region is responsible for protecting vital organs, including the heart and lungs, while also serving as an anchor point for the rib cage.
Components of the T4 and T5 Vertebrae
- Vertebral Body: The large, cylindrical part of the vertebra that supports weight.
- Spinous Process: The bony projection that can be felt along the back, which allows for muscle attachment.
- Transverse Processes: Extensions on either side of the vertebra that serve as points for muscle and ligament attachment.
- Intervertebral Discs: Gel-like cushions between the vertebrae that help absorb shock and facilitate movement.
- Spinal Canal: The space where the spinal cord runs, protected by the vertebral arch.
Common Causes of T4 and T5 Vertebrae Pain
Several factors can lead to discomfort in the T4 and T5 vertebrae. Understanding these causes is essential for effective management and healing. Here are some of the most common causes:
1. Muscle Strain
Overuse or sudden, awkward movements can lead to muscle strains in the back, particularly around the thoracic spine. Lifting heavy objects improperly or engaging in activities that require repetitive twisting can also contribute to muscle strain.
2. Herniated Disc
As intervertebral discs age, they may lose elasticity and become prone to herniation. A herniated disc occurs when the inner gel-like core protrudes through the outer disc layer, exerting pressure on nearby nerves and tissues, causing pain in the surrounding vertebrae.
3. Osteoarthritis
Degenerative changes in joints often lead to osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears down. This condition can occur in the thoracic spine, resulting in inflammation and pain in the T4 and T5 regions.
4. Postural Issues
Poor posture, especially when sitting for extended periods, places undue stress on the thoracic spine, leading to pain over time. Individuals who work at desks without proper ergonomic support often experience T4 and T5 vertebrae pain due to slumping or leaning forward.
5. Injuries and Trauma
Car accidents, falls, or sports injuries can result in damage to the vertebrae or surrounding structures. Fractures in the thoracic spine can cause acute pain and may require medical intervention.
6. Underlying Medical Conditions
Conditions such as scoliosis, osteoporosis, and certain infections may also contribute to pain in the T4 and T5 vertebrae by affecting the structure and integrity of the spine.
Symptoms Associated with T4 and T5 Vertebrae Pain
The symptoms associated with T4 and T5 vertebrae pain can vary widely depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Dull or sharp pain located in the mid-back region.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that may radiate to the shoulders, arms, or chest.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion or stiffness that can make bending and twisting difficult.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations in the arms or hands due to nerve involvement.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions of surrounding muscles that can exacerbate discomfort.
Diagnosing T4 and T5 Vertebrae Pain
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of T4 and T5 vertebrae pain. A healthcare provider will typically follow these steps:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor will begin by taking a comprehensive medical history, asking about the patient’s symptoms, their duration, and any previous injuries. A physical examination will follow, assessing posture, range of motion, and areas of tenderness.
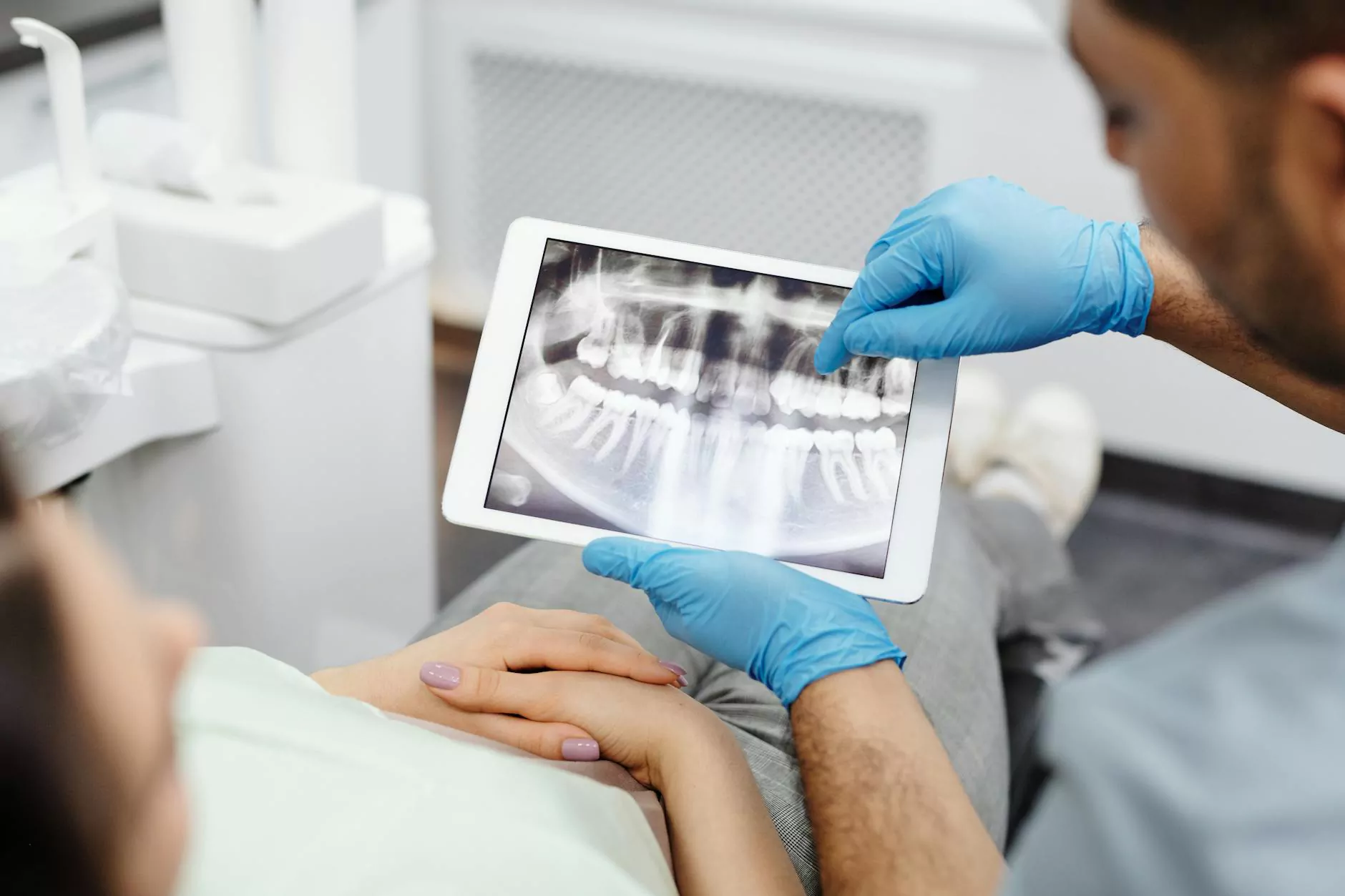
2. Diagnostic Imaging
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans may be ordered to visualize the spinal structures. These tests can help identify structural abnormalities, disc herniation, or signs of arthritis.
3. Nerve Testing
In cases where nerve involvement is suspected, electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies may be performed to evaluate the function of the nerves in the affected area.
Treatment Options for T4 and T5 Vertebrae Pain
There are several treatment modalities available for managing T4 and T5 vertebrae pain. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity and cause of the pain.
1. Conservative Treatments
- Rest: Allowing the back to rest and recover can be beneficial, especially in cases of muscle strain.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice may reduce inflammation, while heat can help relax muscles.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a program that includes strengthening exercises, stretching, and posture training.
- Medications: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
2. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments may aid in restoring spinal alignment and improving mobility. Chiropractors utilize various techniques to treat thoracic spine-related pain, emphasizing gentle manipulation.
3. Massage Therapy
Massage can help relieve tension in the muscles surrounding the thoracic vertebrae, promoting increased blood flow and relaxation. A licensed massage therapist can target specific areas to alleviate pain.
4. Injections
Corticosteroid injections may be recommended for individuals with persistent pain and inflammation. These injections can provide relief by reducing swelling around the affected vertebrae.
5. Surgery
In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures may include decompression surgery for herniated discs or spinal fusion to stabilize the spine.
Preventative Measures for T4 and T5 Vertebrae Pain
While some causes of T4 and T5 vertebrae pain cannot be avoided, several preventative measures can help reduce the risk:
- Maintain Good Posture: Being aware of your posture, especially when sitting for long periods, can help prevent strain on the thoracic spine.
- Strengthen Core Muscles: Engaging in exercises that strengthen the core can provide better support for the spine.
- Warm-up and Stretch: Always warm up before exercise and include stretching to maintain flexibility.
- Ergonomic Work Environment: Adjust your workspace to promote good posture and reduce strain.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting Techniques: Use proper lifting techniques by bending at the knees and keeping the load close to your body.
Conclusion
T4 and T5 vertebrae pain can significantly affect daily life, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower individuals to take control of their health. Seeking timely medical advice and considering preventative measures are important steps in minimizing discomfort and maintaining spinal health. Whether through conservative methods, chiropractic care, or advanced treatment options, relief is achievable. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to your situation.
For further information on managing back pain and exploring treatment options, visit IAOM-US, a resource dedicated to health and medical education.